Aural Skills
Aural Skills
All graduate music students are expected to demonstrate a competency with aural skills relevant to functional tonal music. To pass the exam you need to be comfortable with hearing and identifying functional chromaticism in both melody and harmony. For melody this means that you need to be able to hear and identify chromatic embellishments and modal mixture. Harmonically you need to be able to hear and identify applied harmonies (secondary dominants), modal mixture harmonies, and altered harmonies (Neapolitan chords and Augmented 6th chords).
Intervals - Sample
Identify intervals and their qualities. Press play on the media player below to play a sound file that plays 12 harmonic intervals, spaced about 5 seconds apart. Once playing do not stop or pause the playback. Identify the quality and size of each interval (e.g. Maj 7, or Perfect 4).
Solution Click to expand

Melodic Dictation - Samples
Using the media player below play the melody - up to 4 times. Notate the melody played beginning on the given note. This example is completely diatonic.

Solution Click to expand

Using the media player below play the melody - up to 4 times. Notate the melody played beginning on the given note. This example is completely diatonic.

Solution Click to expand
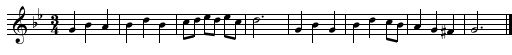
Using the media player below play the melody - up to 5 times. Notate the melody played beginning on the given note. This example features some functional chromaticism.

Solution Click to expand
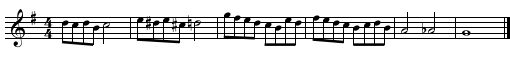
Using the media player below play the melody - up to 5 times. Notate the melody played beginning on the given note. This example features some functional chromaticism.

Solution Click to expand

Using the media player below play the melody - up to 7 times. Notate the melody played beginning on the given note. This example uses non-functional chromaticism.
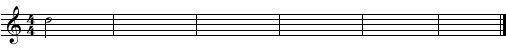
Solution Click to expand
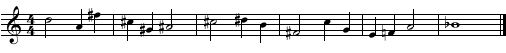
Using the media player below play the melody - up to 7 times. Notate the melody played beginning on the given note. This example uses non-functional chromaticism.

Solution Click to expand
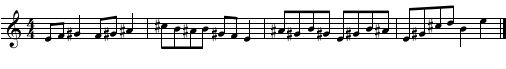
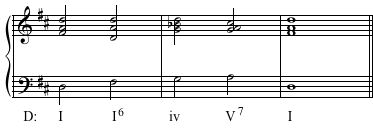
Harmonic Dictation - Samples
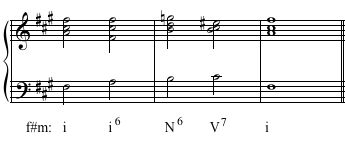
Play each example up to 5 times. Notate the soprano and bass line of the played progression. And, give the Roman numeral functions for each of the chords. The harmonies in the examples will be drawn from the following sources:
- diatonic chords
- applied chords (secondary dominants)
- chords (modal mixture)
- augmented 6th chords (Italian, French, or German)
- Neapolitan 6th chords
Example 1
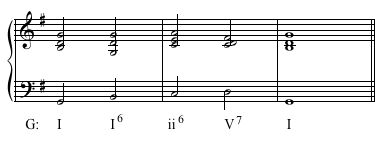
Solution Click to expand
Example 2
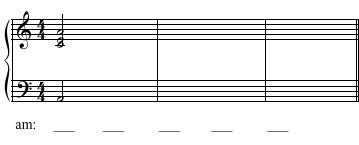
Solution Click to expand
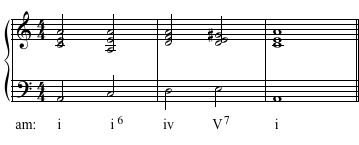
Example 3

Solution Click to expand

Example 4
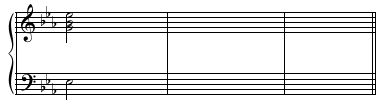
Solution Click to expand

Example 5

Solution Click to expand

Example 6
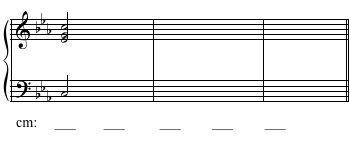
Solution Click to expand
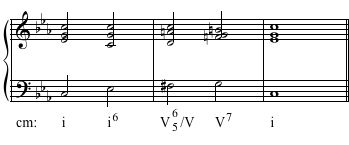
Example 7
Solution Click to expand
Example 8
Solution Click to expand

Example 9

Solution Click to expand